The Universal Laws of Gravity and Repulsion Particles
|
Gravity, is a polarized incoming subatomic particle that applies a force as it passes through a mass to a host mass center. Particle movement creates a wave pattern while rotating 360 degrees about its directional axis thus creating a spiral tube through the host matter as a path of least resistance. The interaction of this subatomic particle movement with matter that is passed through, which creates a force perceived as gravity in the direction of the primary host mass. It is the core of the mass to which these subatomic particles are returning to. The astonishment is that this is only half of the process. As crowding occurs within the core, there is build up of pressure, thus a primary burst of segmented streams, along the equator and secondary emission points about the surface. The individual repulsion particle creates a force when 2 streams interact, thus pushing apart the masses interacting. |
Properties & Origin of the Gravity Sub-Atomic Particle
The Scientific and Off World Technology Page
The laws of gravity that mankind has accepted from Newton and Einstein did provide a foundation and worked for simplistic applications involving the present publicly known concepts of mankind's astrophysics. But as our scientific understanding moves forward, the current accepted theories would fall short, and thus will have be discarded by those who want or shall progress in this field. Using mankind's gravitational formula, lets address the force of gravity between 2 masses and establish a distance between them that is static. If you interchange the positions of the two masses, but maintain the distance between as unchanged, is the force the same? So lets introduce a simple twist, where two independent stellar objects that can replace each other since their masses are equal where each on their own can be one side of the original components of the equation in our example, thus representing M1. One mass shall be designated as M1a having a radius of R, the other designated M1b with a radius of .00001R. This example is being given to mimic a stellar collapse as M1b is similar to M1a only that its radius reduction and its mass is compressed to the volume of a neutron star. Would the flow of gravity be the same on a static mass M2, if there is an interchange between M1a and M1b for M1 as the same distance 1000R between the two masses is maintained? No.
Lets look deeper into mankind's gravitational formulas and concepts. In order for the gravitational wave theory to maintain consistency, the resultant wave maintaining the gravitational force the 2 masses does not change. Diffusion of the gravity wave from the compressed M1b would follow the same principles leading to the flow of gravity at a point as if it were the surface of this mass at the original radius R. Mankind's gravitational law even with Einstein's tweaking does account for the increased flow emanating from a neutron star. As the only mass that could be accreted would have been inside the original surface to disturb the balance of any mass in equilibrium within the local system. But, this could not be the case, as it would have already been captured. This is a direct contradiction all of mankind's theories involving Black Holes ability to consume a mass within the area that was in balance. How does current gravitational laws account for the increase of gravity related to Black Holes? The answer, it does not. Gravity, a polarized subatomic particle that applies a force dependent upon the density of the flow when passing through a mass in direction of a mass's core is only has half the equation, I will complete the equation with the introduction of the repulsion force.
Basic Motion of Subatomic Particles as Gravity Subatomic Particles Pass through a Field
 |
|
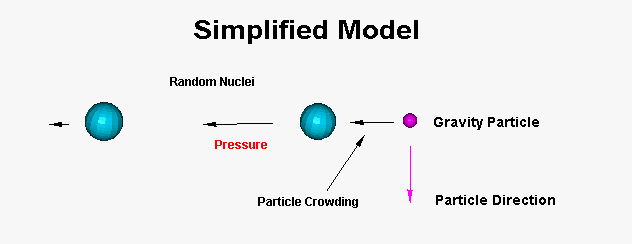
figure 1
In this simplified model, we are isolating the behavior and interaction of a few subatomic particles as a replacement for the original example of nuclei and the gravity subatomic particle within the same plane. This diagram represents the basic motion between the particles due to crowding, but does not account for complex interactions for all motion within the affected field. Here we have a gravity particle entering a zone where pressure between the subatomic particles in the area was in a state of temporary equilibrium. Its introduction into the system crowds the right side of the subatomic particle and to relieve this new force, the area to the left of the subatomic particle, which has a lower density allows the particle to shift temporarily reestablish equilibrium, which undergoes compression towards the far left subatomic particle. What this diagram does not show, is the gravity subatomic particle slight shift away from the subatomic particle due to a field push back. Particle pass through is the process that occurs within most subatomic particle fields as the individual particles cannot permanently alter the path of the gravity subatomic particles attracted to a larger charged masses.
The Creation of Oscillating Motion within a Field caused by the pass through of Gravity Subatomic Particles
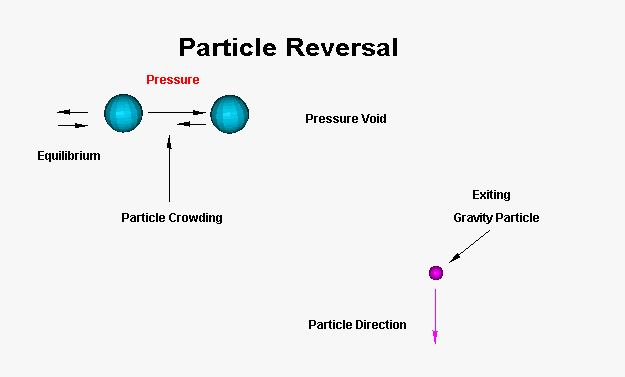 |
figure 2
In this diagram, the gravity particle as it passes and exits the field, the right subatomic particle still approaching the left subatomic particle finds compression building to where advancement stops against the ambient field, but to its rear, a shift occurs due to a drop in pressure as the gravitational subatomic particle leaves a void in its wake. Examining the relationship between the 2 subatomic particles, as pressure builds in front of directional movement from the leading subatomic particle on the left. This forces the subatomic particle on the left to back up until the counter force of ambient field affecting subatomic particle to equalize. Expansion stops and the subatomic particles for an instant holds a relative static position to the other. Now the void to the right offers the path of least resistance, the subatomic particle on the right reverses direction. In its wake, the void allows the subatomic to the left to follow the lead subatomic particle towards the void as dependant to the lead subatomic particle. Momentum continuing until a buildup in the reverse direction stops movement due to natural field crowding by particles on the move from the left. Reversal occurs and again as a pressure void is created in its wake, this area is now the easiest path to flow to. This is the dance subatomic particle participates in as gravity subatomic particles flow through and affect the motion of the field.
Oscillation within a Subatomic Particle Field
 |
|
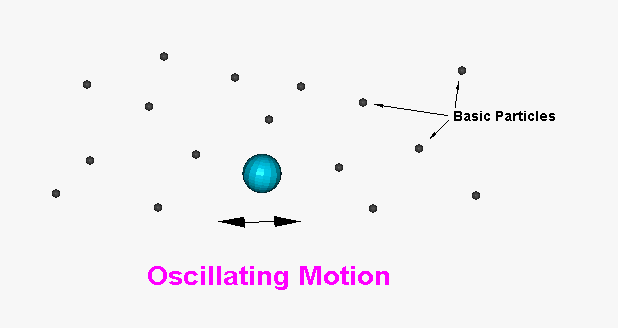
figure 3
The Oscillating motion is a result of subatomic particles and an example of a nucleus as they shift about the field. Moving from one crowded particle area towards a pressure void overshoots carried by momentum into another crowded particle field, reverses flow and the cycle starts all over. These basic subatomic particles, which are the building blocks of all matter and occupy the void of space, provide a consistency to this motion.
Little understood, are the subatomic particles that are related to and maintain the energy level within the nucleus of all matter within this universe as a level on the whole. This is no different than the heat subatomic particles and its known affects on the states of matter. Primarily, it is this action that is responsible for setting a reference base of oscillation governing behavior all subatomic particles in this known universe, including gravity. This oscillation motion occurring within the nucleus and its associated parts within in matter will be known as its resonant frequency or vibrational rate. As the ratio of this subatomic particle in relation to the basic structure of an atom is increased, the properties and laws governing this structure changes. This was learned by the research dept. of the US Navy back in the forties with a disastrous results and a corresponding loss of life. Thus, the concept is the basis for density and parallel universes (details) and the extreme variation in velocity of light.
|
|
Gravity Particles 1. As the gravitational subatomic particles pass through the nucleus of a random mass, they are attracted temporarily to the neutral charge within the core due to its proximity, the gravitational subatomic particle during interaction applies a force (F) as an exponential function related to the density and net direction of flow. 2. Gravitational particles during pass through also disturbs the equilibrium of nuclei of a mass by crowding the affected area, thus the nuclei is compressed as a function of the density of the gravitational subatomic particle flow and the push back from the containment field or matter. 3. Gravity in a snapshot, is the cumulative total of all net directional subatomic particle flows and the related forces applied to the individual nuclei as a collective to a mass for an interval of T for time. The interaction of the gravitational subatomic particles with the mass allows a reference measure of gravity as the interval T approaches mankind's reference of zero. 4. In this Universe away from any significant mass, the flow of gravitational subatomic particles that are emitted from and attracted to almost an infinite amount directions achieves an equilibrium. Thus matter when entering this field drifts, but only due to the force applied to this matter is somewhat equal from all directions, for mankind, they assume the phenomena of weightlessness or the absence of gravity without understanding the total process. |
|
|
Behavior of a Gravity Particle During a Pass Thru of an Atom
Step 1: A random approaching gravity particle where field density compression allows a pass within a zone where the proximity of an attractive charge residing in the core of the nucleus allows its path to be altered. Step 2: As the gravitational subatomic particle passes through electron field of the atom, but before the nucleus is penetrated, there is a small controlled loss of the positively charged portion due to exposure to the electron field, a snap exposure for a charge equalization. Thus tweaking the directional flow of the gravitational subatomic particle closer to the center of the nucleus. Step 3: When the gravitational subatomic particle enters the nucleus, it gains back a fractional portion positive related charges from a loss to the electron field pass through as it temporally attaches to the core and its neutral charge, although it is quickly expelled due to momentum and overall attraction to a more dominant attractive mass as explained in the next step. Step 4: As other gravity particles follow the same path, pressure builds from behind and the gravity subatomic particle clumps temporarily and easily adapts a repulsive force from the core as the carrying capacity is exceeded with the overall outside attraction and is ejected from the nucleus while releasing another frictional force during the pass through again in the same direction. Step 5: As the ejected gravity subatomic particle enters the electron field again, the positive charge acquired from within the nucleus is not only lost, but even more to the electron field as the charge is sweep away by the field reentering the nucleus. Step 6: The gravity subatomic particle returns to its original path with an almost undetectable increase in the charge differential to neutral due the minute loss of positive charge, which bled away in an incremental fashion during the pass through towards the dominant mass with the greatest differential within the zone of influence. |
figure 5 For more details on the atomic structure and its electron particle field, consult astro33.htm.
A Blueprint of the Universe using the Concept of an Encapsulating Bubble
The Isolation of Gravitational Field of Influence
So lets examine how gravity affects the Universe on a whole and then we can break it down through its many levels as this process of gravitational subatomic particle flow controls motion within the galactic clusters, galaxies, stellar clusters, multiple to singular stellar systems, planets, to surface gravity and control of if any satellites or moons.
For a simplistic explanation we will use the bubble as the basis for gravitational field containment and sphere of influence when explaining the universe on our density level only. Although, as for universe on a level which encompasses all, it is here that I have only a partial answer. The universe, represented by the initial bubble is expanding, always a part that is being created as the cause. All the while there are sections regenerating from a black hole to a localized big bang. All of those concepts I can understand. What is beyond my understanding is that the surface of the bubble is infinite, yet if at the edge, you would have the appearance of being in the middle of the universe as a view in all directions would continue as far as the eye, instrument or probe can see. Always expanding as matter is created where there was none. Is this our universe, yes. Can it be totally explained, no. This is not chaos organizing by chance, but God organizing the chaos into this universe and for some this could not be unintended. Although, a level of doubt is there to allow a choice.
As some of you know in my life, God is not faith, or just a belief, but an integral living interaction within my being. Now this is not a statement to sway the reader as with the religions on Earth do when you enter their lair, because you have a choice. But you know where I stand. I respect your choice or lack of, respect mine, moving on.
Once inside the initial bubble we can explain how the galactic clusters behave with each other due to gravity. The Universe differs from a Galaxy in that the Universe constantly expands through creation. As with a Galaxy it is a cycle of compression due to the black hole until a point is reached where expansion is initiated by a local big bang. This is the process of renewal in the universe, no different than the recycling program on Earth. Each Galaxy is encapsulated within its own bubble and are under a different set parameters.
Within the Universe, the bubbles containing galaxies separate due the principles of particle crowding to maintain equilibrium with the creation of new matter there is a natural expansion bubble containing the entire universe in response. The creation of matter is what maintains a pressure barrier that sets a limit to expansion for a galaxy, thus the individual bubble. Within the galactic bubble the natural forces that scientists are generally familiar with, take form. The field of gravity particles expand against the density of the universe and are turned back, thus the containment surface shell of the bubble representing the galaxy. This bubble expanding the influence moves the entire bubble as one without affecting the more intense internal gravitational field.
Gravity shapes the galaxies from its creation as an expanding ball of mass explodes out of a black hole and this is a key to determine its relative age. Although, the gravitational force does allow the flash of creation to be seen, a pressure wave against the interstellar medium can give it away if one knows what to look for. Rotation from the expanding former black hole throws a larger portion of the mass out along the ecliptic as the youngest galaxies take the form of a spiral. With the emitted streams pushing the new formed stars along in the distinctive arms.
As the gravitational flow increases over time due to the accretion of stellar mass into the black hole in the center of the galaxy, the emissions streams from the central core intensify and the distance between them shrink, cannibalizing a number of them through merger. Until just two are seen for the medium sized galaxies. Compression continues to reshape the spiral as gravity shifts the stars inward. They morph away from the ecliptic due to equalization. As gravitational pressure forces the outer edges of the spiral to collapse back upon itself, crowding occurs along the ecliptic pushing the stars inward and further away from the ecliptic top escape the pressure. Thus shifts into more mature elliptical galaxy then into the final shape a shrinking globular galaxy as gravitational flow increases to a more extreme level. This the sequence of a galaxy from creation due to a local big bang to its death total absorption by the central black hole all controlled by gravity. Larger more massive galaxies have a more complex interaction with gravity, leading a different form after creation to compression and will be covered in a future paper.
Inside the galactic bubble, the gravitational field of influence is controlled by the primary black hole subatomic particle expulsion intensity and its core rotation. With the perimeter of the bubble set due to equalization of the particle expulsion and the push back from interstellar medium compression. Rotation is driven and dependent upon core emitted stream force, density, retained neutral charge and the total galactic stellar mass being pushed. This is what primarily determines the period of galactic rotation. Swept along with the individual stellar clusters are the stellar systems as one fluid mass. Again, we can breakdown the gravitational field of influence to stellar clusters, subset of individual stellar systems as a subset within the clusters and the independent stellar systems.
A stellar cluster maintains the same gravitational field principles of a galactic formation, but its sphere of influence is limited by the central gravitational mass, which maintains the cluster formation. Primarily is dark due to the accretion of dead stellar objects and in rare cases is dimly lit as sporadic fusion initiates due to extreme compression. The central mass sets the parameters for the next bubble, which is in various stages of development, ultimately evolving into a black hole. Basic observation gives a clue as elliptical cluster presents an early stage, loose globular cluster early medium, a cluster moving from dense to a more dispersed format is a medium stage, and a tight globular stellar cluster of high density, represents latter stages of stellar cluster formation.
Within the stellar cluster, dependent upon the central mass, we now see that the parameters are distinctly defined by the gravitational field and maturity of the cluster is responsible for its shape. Rotation is always a factor of the core, as the many diffused emitted streams due to a low rotation to radii of the cluster. So the stars are sweep along as a group of one. The stellar systems themselves also create a self contain bubble of gravitational field influence. It is here that individual stars within the cluster and independent stellar systems within the galaxy behave the same. So we will cover both as one.
As with all of the preceding bubbles, the most intense pressure produced against the interstellar medium is created by the stellar system. A complex multiple grouping of stars creates an almost infinite about of variables as to the internal flow of gravitational particles. So as a basic step, we examine a system with 1 star and planets. Do not confuse what seems as a single stellar system containing our Sun with its planetary orbital anomalies showing the affects of another gravitational source is truly binary system with its dark companion in this example.
Within the solar system the star dependent upon its mass controls the force of emitted streams that not only maintain the distance of any mass within the field of influence, but also the rotational period of an object. This is based on stream intensity, volume of subatomic particle flow, the number of streams, and the sustained rate of rotation against the medium at expulsion. All objects are sweep along matching the direction of rotation of the primary object.
Drilling down to the planetary level, a gravitational field bubble within a bubble forms, which affects the motion of all moons and objects within the planetary zone of influence. Even though as other subatomic particle flows are present, outside gravitational sources has achieved equilibrium, the forces applied to all masses within the zone nets no overall change, unless an unexpected force is introduced outside of normal conditions. Thus, the local primary mass and its gravitational repulsion subatomic particle flow is now responsible all motion within the affected area. There is a tipping point that establishes balance one way or another, it is this response where flow is established overlapping the established equilibrium. The field of influence affects distance and placement of moons, their periods of rotation due to repulsion stream particle torque and dependent upon time of capture, mass and point of entry its angle of declination off of the equatorial plane of rotation. All of which is reliant upon when and where a mass is injected into the system or initially settles into equilibrium, an orbit.
The final major layer is planetary or in some cases moon atmospheric containment, where the gaseous fields are formed by a slow process of emission as its mass cools or leaches from its oceans and some cases the surface crust. Compared to a star, where its atmospheric projection into interstellar space is a balance of solar wind emission and its total mass to volume, which dictates gravitational return flow. The secondary atmospheric boundary is held in place as gravitational charge particles caught in a neutral zone between gravitational masses, build as a static barrier with the push back against expansion due to dark matter and the interstellar medium. It is here gravitational subatomic particles applied a force to an atmosphere or in the case of a low mass stellar object, stellar wind as tries to pass through the static zone, atmospheric loss is slowed, thus a containment force. This is the basis for planetary atmospheric field and its confined zone of influence.
This is how gravitational sub atomic particle flow works on a local level, but maintains an overlapping part of many upper levels or layers of the motion of attraction and repulsion within the universe. As there are many gravitational flows within the universe all working as one. For a mass, it is primarily a local field event as each outside bubble has an exponentially less of an affect on the mass as a part of the whole field. It is this principle that is behind the self contained gravitational fields created on interstellar craft. By increasing the gravitational particle flow against the flow stream towards the local mass, all objects respond to the local field inside the artificially created bubble, thus the lack of G forces from the flow of outside gravitational fields.
The concept gravity has been elusive to mankind, as most in academia can describe its affects and has formulated an equation where the math seems to fit the effect, but almost all have no clue of how it really works. So moving on, lets examine what really creates the force of gravity and how it works.
Gravity is a force, created by a select group of polarized subatomic particles as they flow through all matter. Where the collective sum of all forces at any given instant in the flow of time, is applied to any particulate of matter, to any mass, of any size, creating a single force with a defined direction and intensity towards the core of the dominant mass controlling the general field that establishes a bubble separation from all other gravitational subatomic particle flows. Gravitational subatomic particles flowing as an organized field are attracted or diverted temporarily towards the base neutral charge residing in any sub particle, atom, or smaller mass along its path. Ultimately to clump due particle charge differential and gather as one, flowing towards the attractive neutral charge generated by core of dominant mass. This field is described above as the containment bubble.
The differential between the adaptation of the neutral charge and the bleed off of the positive factor of the charge related to the gravitational subatomic particles is a determinate of the intensity of the neutral charge from the dominant mass and distance coupled the subatomic particle charge loss and its resultant differential. This results in a varied field of gravitational subatomic particles with various charges once pass the thresh hold of attraction flowing towards the dominant core. Resulting in coupling or clumping of gravitational subatomic particles flowing to a single overall mass.
As a start, we examine a local area where entire area is under somewhat uniform pressure creating motion as group, but within the general area at the edge of field containment, the net force applied in any direction is an overall null (weightlessness). Where there is random motion, but the area affected maintains static format with no organized motion or flow towards any primary source.
The individual particulates of matter contained within or floating about the interstellar medium all have a base charge, although infinitesimal, is enough to divert or attract the direction of all affected gravitational subatomic particles to pass through its core according to a set of spatial and density parameters. Proximity and density of the gravitational subatomic particles to the matter is what determines the volume of particles that engage or pass to the outside. It is this repeated pattern that changes a random floating gravitational subatomic particle as a slow bleed of the positive charge is loss to pass through. Increasing the differential towards the negative from the established base charge. There is a point where the random float due to the increasing charge differential, changes to a directional flow towards the source of attraction a dominant mass. This point of change for the gravitational subatomic particle can be anywhere within the sphere of influence (the bubble) all dependent upon the intensity of the neutral charge emanating from the mass, the differential on the particle and its distance from the mass. This is how a gravitational field towards a dominant mass is organized and established.
The base charge of any particulate or significant mass is the final piece of the puzzle that mankind has sought in linking gravity to his quest for theory of everything or the Unified Field Theory. It is this principle, that the flow of subatomic particles related to magnetism and gravity both share a common field within the core of matter or a mass and the atom itself. Where magnetism, a stronger force builds a potential charge differential from the core charge, once ejected through the north pole by crowding and repulsion from the shared like charge, only to flow back to the south pole or ground of the core. Gravity, adapts to the intensity neutral charge of the core, all dependent upon the flow, the interval of time the gravitational subatomic is in general contact of the core and the mass. Upon ejection a random subatomic particle could flow to the edge of the galaxy and in some cases to the edge of the universe. It is the intensity of the neutral charge dependent upon mass and compression of its matter within that influences the flow of gravitational subatomic particle.
The charge that gravitational subatomic particles flow to is the neutral charge that occurs within the center of every polarized subatomic particle, atom and mass. Does not mankind's description of electrons of once a positive potential is achieved by natural forces or induced, there is a established flow to a neutral point or ground where the charge is in equilibrium. With gravitational subatomic particles, the lose their charge to the ambient interstellar medium and random mass pass through, increasing the potential differential from neutral is new.
As described in the paper the Atomic Structure the electron stream as assumed by mankind does not revolve about the atom. The electron stream is an integral part of the nucleus, thus maintaining the overall neutral charge within the core that maintains the structure, the nuclear force in this case. It flows through the core of an individual atom, but when a mass builds, this flow intensifies, couples and flows the central portion of the mass.
Charged subatomic particles related to the electron flow around, about and through the nucleus as seen in figure 5 are ejected at the north pole and reentering at the south. The point of equilibrium for the atomic structure is the central area of the nucleus where the positive charge and in cases of neutral components related only affecting volume of flow and the subatomic electron stream meet and the over charge is neutral. A change in the behavior of subsets of subatomic particles becomes apparent a mass grows to point where its core under goes compression. The mass has pass a critical point where the overall volume neutrally charged passing through the center of this mass affects other subatomic particle flows and field flow essentially flows like one. This is the general concept.
You have been introduced to subatomic particle clumping for the gravity subatomic particle. In addition, the gravity subatomic particle is a unique grouping or subset of particles itself where polarity on one extreme tops out at neutral, the adaptation of the ambient charge within the nucleus of the atoms of any matter and return flow is determined by the loss of this charge in the thin dark matter field of outer space and the random contact with electron related fields of sparse atoms or cosmic mass. Gravity is a weak force only in the principle that its relative differential creating a polarize charge is due to a lose of charge shifting away from neutral.
We will now cover the relationship of mass and density and its affect on field intensity through an increase refresh rate (the interchange cycle of incoming flow, gravity and expulsion, repulsion) within the core of a mass. Where the total mass and its density determines the intensity of the attractive neutral charge, but the affected area of the mass that allows a transfer process of the gravity particle to a repulsion particle to increase. Thus the basis for the refresh rate of mass to be established. It is here that the flow rate of gravitational subatomic particles intensify setting the parameters of the incoming field related to the mass.
Within a simplistic mass, the size of Earth and for a basic explanation this mass will be homogeneous in composition, but density will naturally increase as a particle approaches the core. All matter down to the atomic structure of the nucleus has a natural inherent field of subatomic particles that are ejected and then slowly captured and flows back to source such as a central point of an atom, a cohesive grouping of matter, but ultimately a cosmic mass. The generated gravitational field is dependant upon the size and concentration of a mass and distance from other masses in which the dance between them is in equilibrium or is captured and it is the dominant mass that controls the local field flow. We will cover what principles of mass attracts the gravity subatomic particle and what force allows equilibrium to be attained between masses. The subatomic particles although polarized slowly adapt or lose its faint charge ambient to the general electron field charge of matter floating about interstellar space, of which there is extended contact.
A mass is a collection of atoms, as it grows to planetary scales several factors organize. It is the electron subatomic particle flow, which is dependant upon the quantity of stable atoms and the combined resultant neutral charge flowing through a compressed core that controls gravity. So how does this process work?
The key feature of the uniform combination of subatomic particles is adaptation of a polarized charge and on the counter side, slowly shedding the charge when removed from its source the core of a mass. As our explanation starts at the core of a mass, we will examine the affect of neutral charge first, then consider the intensity of this charge an its linkage to the volume of mass. In essence, mass and more important its compression at its core. It is within this zone where subatomic particle flow related to a neutral charge through atomic structure increases as a result.
So you are asking what neutral charge is flowing within the atom as not all atoms contain a neutron and the overall charge on the nucleus is positive? First you must rethink all current theories of mankind concerning the structure of an atom. With no guide or visual reference scientist assumed matter related to the electron revolves around the nucleus, their example the Sun and planets this seemed safe as a theory as all could related. Did you consider if an electron is shed or flows like electricity how does it return to its orbit. How is electron orbital sharing achieved and the properties of a molecular compound similar if only the electron rings interact? If this is not true concept of the atom, what is and how does gravity become part of the process?
The neutral charge within a mass's core is greatest at the core due to the natural compression and the combined flow of the electron subatomic field of matter within the zone when compressed on the scale of cosmic masses. The larger the mass, the more intense the neutral particle field extends and the greater the flow through this point. Because the gravity subatomic spends most of its time drifting in the thin interstellar medium and contact with the neutral charge only occurs as a pass through, which applies a force in the direction of movement or capture in the dominant gravitational mass's core within the established fields before natural separation initiates, expulsion as a repulsion particle. The key here with the neutral charge is that it neutral because the flow of subatomic particles of a negative polarity passes through a nucleus with a positive charge, thus equilibrium. For the gravity subatomic particle it loses its neutral charge to the interstellar medium as charges related to the electron stream is where most contact is spent. The longer the exposure the greater the shift towards the negative field. This bleed off of the neutral charge is explained in detail under the repulsion particle. When a large mass is introduced to the field there a differential between the negatively polarized gravitational subatomic particle and the neutral charge of the mass's core. The more intense the charge, the greater the influence is projected for the field to be organized for attraction to that mass. Thus this is the basis for gravitational flow.
Because the gravitational subatomic particle is polarized there are 2 primary features. When its ambient environment has a common charge, the particles spread or repulse each other. In the vast areas of interstellar space between cosmic objects, the medium contains dark matter, unorganized subatomic particles, which are the basic building blocks of matter and other elements. Where organization has occurred and is maintained, the vast areas low density space is controlled by an extended field of their electron related subatomic particle flow of elemental matter in comparison to the neutral charged core of a atom. The gravity particle bleeds its charge to that of an electron stream of outer space slowly as the applied field charge infinitesimally weak. When a charged particle is introduced to a another charged field the weaker flows to the dominant as a process of equilibrium. This is why the gravitational subatomic particle develops a charge differential to the core of a mass. But due to the varying lengths of time and random contact with a mass's core, equilibrium is established in the interstellar medium where the combined force of random gravitational subatomic particles and its counterpart passing through a mass is null when a mass is away from the organized field flow of a cosmic object or for mankind weightlessness. As a significant mass host with a large neutral charge flow, gravitational subatomic particles flows toward this differential. Once attached to the neutral charge there is a modification, as the gravitational subatomic particle adapts the neutral charge and polarizes in favor of the mass's core. The cascading gravitational subatomic particles adapt and flip or bind north-south pole into alignment. Thus this polarized feature the gravitational subatomic particles attracted into the core as a whole clumps or accumulates within the core neutral charge field, which a brief concept was introduced in the reference above.
So how does this neutral charge affect a gravitational field range and intensity? The larger the mass, the greater the neutrally charged flow attracts gravitational subatomic particles to clump about the core. If the flow was light, there would only be a subtle change towards the neutral flow within the core of a mass, thus the clumping of incoming charged cascading gravitational subatomic particles would have a smaller differential and an equally decreased field influence.
When a mass is compressed to the extreme, such as the present day gravitational concepts of a neutron star another factor affects flow shall be introduced, core refresh rate. It here the carrying capacity of the core and its related volume can not handle the influx of gravitational subatomic particles related to near field gravitational flow. Thus there is a point the accumulated gravitational subatomic particles achieve the same like charge. Where upon they build, to point a where containment adaptation of the neutral charge dependant upon the flow creates a repulsion force within the inside component clump of like charged gravitational sub atomic particles. To relieve the pressure there is a breach of the containment field and ejection initiates a set powerful streams exiting the core and eventually the mass. The cycle of this replacement is directly linked to the volume and density of the mass, thus the term gravitational subatomic particle flow core refresh rate. When using a reference sphere, volume is critical as the relationship between containment and expulsion increases exponentially as a function of the decrease of the radius. Density of the mass invokes a neutral charge which is compressed within the mass's core, but there is a limit to increasing the density or intensity of a gravitational subatomic particle field. This is why the refresh rate is responsible for the greatest increase in gravitational flow. It is this property that allows a black hole develop, not an increase in gravitational subatomic particle field density attracted to large neutral flow, but through a rapid core refresh rate due to the decrease in radius of the original mass.
What factors can affect the gravitational core refresh rate?
The volume of the sphere is primary as the radius of the active core due to density to the total average radius of the mass. A point is reached where natural gravitational subatomic particle flow related to a mass's incoming field saturates due to subatomic particle crowding. So as a mass shrinks in volume as when a stellar object nears the end its current form, there is ratio relationship that varies between two areas of the mass as its density increases. The active core area where the transfer of the neutral charge due to proximity occurs and its imaginary spherical surface containment shell vs. the total mass increases as a ratio. The build up time interval as pressure created from the inflow of gravitational subatomic particles to breach of containment decreases. In order to maintain flow the refresh rate or interchange of inflow versus expulsion creating a void increases inflow all to maintain a field equilibrium. This is the factor behind the intense gravitational fields of neutron stars and black holes.
Secondary, it is the original composition and density of the mass where the intensity of the neutral charge flowing through the core initiates gravitational field flow as a base. As the mass is compressed, its original state of composition and initial density takes a lesser role in affecting the field refresh rate.
So how does the large neutral charge develop and what factors of mass contribute to gravitational subatomic particle flow and its eventually clumping within the central portion of a mass?
The gravitational subatomic particle has a natural self contained flow that forms a distinct field even at the atomic level. As this is one of the properties of the Unified Field Theory. It is only when the cascading affects of this flow from a large mass, in which a field moving to the central area starts to compress the outer areas of the mass towards the established central point. As a mass grows, compression at the core continues to accelerate and the first factor that affects gravitational flow increases to a point where a significant terrestrial or solar field is established. This is a point where the forces applied other matter within this field are affected and outside gravitational forces affect the total field as one entity. Where movement of the individual masses within react to the local field.
The process within the core that exponentially increases gravitational subatomic particle flow, when compression within the core constricts naturally the space between the molecular structure of matter. This is when a new factor affects the flow. The key here is to force the molecular structure of matter to share their electron streams due to pressure. It is here that the shared flow within the compressed core builds an intense neutral charge as the fields couple. A simple comparison would be the charge is maintained (voltage) [neutral charge], but the flow of charge increases (amperage) [neutral charge intensity]. The next level of compression moves the sharing of electron streams to a point where the process of transmutation of matter to heavier elements and its by products antimatter and primarily the release of heat, photon and other subatomic particles are the result. The is why some planetary cores that has achieved a specific mass are still molten billions of years after their creation. The process maintains a molten core, but in most cases the heat is lost to outer space, only in the larger planets it is possible to be a net producer of heat as with Jupiter and rare cases light on other objects.
If we examine the laws of gravity we will find that as the radius is reduced the gravitational containment does not keep pace with mankind's density formulas, thus discrepancy in the current hydrostatic equations of a stellar mass. This will be addressed in the latter portions of this paper.
 |
Repulsion Particles
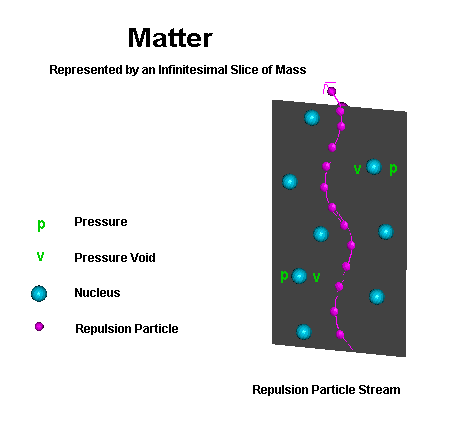
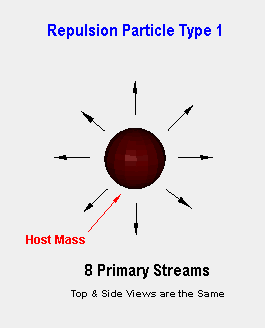
The repulsion particle streams emitted from the core of a mass are only different from incoming gravitational subatomic particles due to the adaptation of ambient core neutral charge, which gravitational subatomic particles lose while they transverse interstellar space. Because of their like charge, coupled with the constant influx of gravitational subatomic particle flow pressure builds due to crowding within the core of a mass. They are released in pulse like bursts from the core of a mass in a tight coherent sinusoidal stream of particles as they break the incoming gravitational core containment barrier. This results in a 360 degree spherical release, where the number of streams emitted dictate the distribution about the sphere as a function of equalization. If the mass exhibits rotation, then expulsion for a rotating mass increases within the zone from the centrifugal force transferred along the equatorial plane dropping rapidly as one moves towards a pole. Interaction with a mass within the near field exhibits no force applied to the mass as the nuclei are parted by a concentrated pulsed streams of repulsion particles due to the like charge of the core. Rather than pressure that causes the stream to rip through a mass or field as each repulsion subatomic particle follows the wake created by preceding repulsion particle as illustrated to the left. |
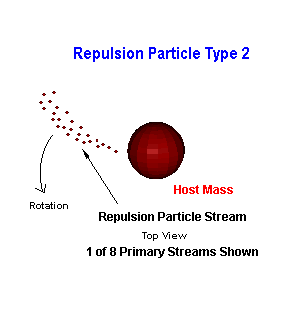
With the introduction of Repulsion Particle Ejection occurring in 2 primary ways random intermittent dispersal about the mass and a more concentrated bleed off about the equatorial plane of a rotating mass. Lets address both in more detail.
In a brief Synopsis, the first type is the repulsion particle ejected randomly about the globe of the primary source where a gravitational containment field is established and its primarily function regulates the distance between the masses within the local gravitational field (bubble). The second type of emitted repulsion particles are only different by the point of emission. Where stream density, rotational torque inherited from the emission mass affects the orbital motion of the attending satellites of the primary mass within the affected local area. This is how stellar objects can sweep the planetary and subcomponent cosmic objects to establish orbits about the primary gravitational source in most cases a stellar or multi version of the system. But planets, which independently can locally control is own captured moons. Evidence of these streams exhibit themselves as the number stars, which are segregated in the early formation of galaxies resulting in the formation of arms contained in spiral galaxies.
Reviewing, several factors control the inflow of gravity particles and their expulsion as repulsion particles. With core compression initiated, a shared electron stream and its field of influence is primarily dependant upon the neutral charged flow, a derivative of the polarized charge in the atom flowing pole to pole in the mass itself (the total mass has a direct affect on compression and total amount of electron streams available for shared flow). As explained in the structure of the atom, the nucleus where the strong charges that hold together its structure, are a compromise where the intensity of the neutral charge is the result of this equilibrium. The stronger the flow the easier to maximize the charge on the incoming clumping gravitational subatomic particles as they come in contact with the stream inside the core of a mass.
A charge flows from the neutral stream to the gravity particles and the transfer of this energy is directly related to the flow of neutral charge and density of the gravitational subatomic particle clumping about the core. Once charge parity of particles is achieved, the charge that attracted them to clump around the core of the mass switches to repulsion. The charge on the repulsion particles at or near the maximum clump as small differentials between the particles cause them to group and grow. They segregate maintaining a static equilibrium between the pods but random positioning due rotation and core eddies about imaginary spherical shell within the core of most cosmic masses. Neutron stars, black holes and similar intense extreme gravitational fields sources have different set of rules, which will be cover in another paper. These charged pods build as affected repulsion subatomic particles migrate away from the neutral charge stream, as the like charge now repels with a greater intensity due to growth. The pods continue to migrate away from stream as the size the charge intensifies as more particles gather. This continues until these pods reach the edge of the incoming gravitational containment field. There is a breach once the outer most tangential point of the pod makes contact with the imaginary shell defining gravitational spherical containment around the core. This creates a tight stream of particles repulsed from the like neutral charge of the core. Force of this stream is related to the neutral flow and the potential force of the containment field in conjunction of refresh rate vs. void left accelerating the build up of incoming gravitational field flows.
The repulsion stream has a different effect on matter than gravity. Once a breach in the containment field surrounding the core occurs, a stream flow initiates as the following particle moves into the low density wake void left by the preceding particle. This continues until incoming containment pressure builds to a point where lateral pressure at the breach point is constricted and then closed. Its affect on matter at close range in general is transparent as a tight stream following the same path does not apply a significant force as the nuclei within a mass just shifts out of the way.
Near Field Effects of the Repulsion Particle on Matter or a Cosmic Mass
The repulsion subatomic particle exhibits some of the following new characteristics not yet seen by scientists. Any mass encountered at close range (this range is dependant on the size of the host mass, ratio of gravitational subatomic particles clumped about the core to the flow of the neutral charge within its central core) while exiting the primary mass is not effected, since the repulsion particles emitted tend to rip through or brush aside the atomic structure within a minor mass due to speed, density and charge of the particle ejection stream without applying a force to the pass-thru mass.
This is accomplished as a compressed stream of ejected repulsion subatomic particles follow in each other allowing a minimal push to affect the mass. Within any mass once a path is formed and maintained, particle movement follows the preceding particle in close proximity due to the rear wake which creates a pressure void thus a natural flow is formed. Interaction with the mass and repulsion subatomic particles during pass through is minimized. Also the like charge of the repulsion particle is the same as the neutral charge residing in the atomic structure of all matter. In a small mass equilibrium is maintained with subtle variations that change the path due to the principles of particle movement. The key here is that the nuclei, which comprises the mass is pushed to the side, thus the repulsion particle rarely passes thru the nucleus of matter which results in applying a force in the direction of movement near the host mass.
When encountering and near field cosmic object, the repulsion streams tend to bend around it in general, but a change in its path does occur based on the size of the mass and distance from the host mass. As a large mass approaches, the streams diverted press against others and there is a push back by other streams at first along the outer perimeter. Until there is a point of repulsion between the streams due to crowding their path can no longer altered any further under existing conditions. This forces some of the streams to directly encounter the core of the mass. This encounter is what creates the force of repulsion from streams engaging then the affect of pushing away the like charged core of the cosmic mass preventing moons from crashing into a planet due to gravity or planets from being absorbed by its star. The distance between the masses are a factors of equilibrium, the point of repulsion and the incoming gravitational flow to the primary mass. If the repulsion force can establish a distance between masses, then what accounts for an orbit and of secondary concern in our system planetary orbits are elliptical, yet what we have learned leads to a conclusion, orbits in a single stellar should be circular with subtle variations along the path?
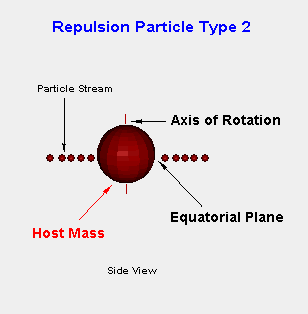
In the second type of an emitted repulsion particle, how and where it is released dictates responsibility for rotation of a satellite, planetary, stellar or galactic system. As the core of the host mass rotates, the liked charged repulsion particles crowd the equatorial area due to centrifugal force and are pushed to the edge of the core. At the edge points of pressure develop, the quantity of these points is determined by the permeability of the containment field, breach points decrease along the ecliptic as the field hardens. For the type 2 repulsion particle, expulsion within the equatorial plane allows for rotational torque to be inherited from the direction of the rotation of the host's mass core to repulsion subatomic particle streams. As these streams flow away from a mass rotational torque is lost as density decreases and it is these streams that the sweep planets or moons ahead of its motion as the cores of these masses try to avoid the similar charge residing within the repulsion particles streams.
Now lets examine the cycle of gravitational subatomic particle inflow and a repulsion subatomic particle bursts and the process of alternating spherical to equatorial plane repulsion subatomic containment breaches, the refresh rate. When a breach occurs in 2 or more location along the rotational equatorial plane there is a pressure void left in the wake of the expulsion of repulsion subatomic particle streams. The imaginary spherical containment shell shrinks in response, the build up is different this time as rotational torque is busy backfilling the void left by the last ejection. This time a lower density breach occurs at many points about the spherical shell in a general release. Again the spherical shell collapses with pressures some what even about the core. Focus flips back to the rotational equatorial plane where pressure builds and the breach occurs here and the cycle repeats. This is the refresh rate the period of time to complete ejection along the equatorial plane and the whole sphere and its related inflow of gravitational subatomic particles as core replacements.
The Neutral Charge Bleed off into the Interstellar Medium
the migration of repulsion to gravitational subatomic particle
The adaptation of the neutral charge flowing through ordinary matter is applied to gravitational subatomic particles. Once ejected as repulsion particles a change occurs. As they remain over time drifting over vast regions of interstellar medium, the charge bleeds off. In outer space the vast area and field charge are related to electron subatomic particle flow. Examining how the repulsion particle loses its neutral charge, lets look at the atomic structure of single atom of matter and the interaction that takes place as the repulsion particle passes through the atom's electron subatomic particle field. The basic principles behind the concept is the same with all matter only the intensity level of flow and field strength changes. As the electron stream leaves the north pole of the atomic structure the positive potential flow towards the south pole attracted to a negative differential. Does not electric current carry a potential, yet it is comprised of flowing electrons. The gravitational-repulsion subatomic particle behaves in the same manner, as it engages an electron stream its charge on the particle edge rips away and is attracted to the negative pole due to the differential between neutral and that polar charge. Flow is established. On the atomic level there is a close balance within a field of separate atomic structures. Where a gravitational subatomic particle can slowly loses its charge by being in close proximity, but never be part of the field on a singular atomic level due to crowding. Over time this creates a potential differential between the gravitational subatomic particle, and dependent upon loss of charge and distance from a mass and its intensity of neutral charge, a return flow is established to this dominant mass within the local area. This why a moon can have its own gravitational field affecting matter on its surface yet revolve and be a part of the gravitational field of a planet, then a star, sometimes a cluster, then galaxy, and ultimately the universe.
The Interaction of the Return Flow along the Outflow of the Dominant Mass at or near the Equatorial Plane
Gravitational-repulsion field has a sub process, it is a outgoing repulsion subatomic particle flow which creates a thin ejected particle stream within an established ecliptic plane of significant mass. As the gravitational subatomic particle field returns to this mass, there is a turbulence that develops between the 2 flows that provides order any mass in equilibrium rotation of the dominant mass ( a stellar mass with planets or debris orbiting within an established equatorial plane of that mass).
Lets examine our solar system as an example. As the gravitational subatomic particles return towards the neutral charged center of our Sun, they encounter the exiting repulsion subatomic particle streams. Within these exiting streams there are pressure voids as the flow emitted from the Sun is not coherent. As the return flow field compresses, there is a flow towards these low pressure voids. Thus at the point of interaction between the 2 flows, the incoming sandwiching the outgoing, a circular flow from the incoming curls in the direction and joins the outgoing repulsion particle flow by taking advantages of low pressure gaps. The result is a force applied to any mass near the ecliptic plane towards its point of neutrality. This why planets in a mature stellar system are located along or within the ecliptic plane. For more details, please read Orbital Plane and Motion.
Gravitational Field of Influence
We have reviewed that the primary cause for organized motion of the gravitational subatomic particles is the differential from the base neutral charge loss to interstellar medium. The neutral charge, an inherent property that is related to mass, its charge intensity dependent on flow through the mass, where compression, volume, and composition of matter are the primary factors. The subatomic particle related to gravity-repulsion loses is charge as a factor of time spent discharging its neutral charge into the interstellar medium, dark matter and its related electron stream. This charge gap is the differential and distance from the particle now determines flow. So how does this affect the field of influence of a dominant mass and its relationship of motion to the universe?
Gravitational subatomic particle flow and its effects within this universe, is a balance of delicate particle flows related to intensity of the neutral charge within and emanating from a mass. It is the distance and the differential charge on the gravity subatomic particle that establishes the field of influence. So we start our examination of this process at the galactic level.
The primary core formations of a galaxy is either a dense collection of stellar masses establishing a central point of gravitational subatomic particle flow, a somewhat static black hole in relation to the total motion of the galactic mass or unique combination of the two gravitational centers where there is an active zone of accretion of stellar mass into the central black hole.
As the repulsion streams are emitted from a collective of masses that form the gravitational center of a galaxy, they coalesce and organize. It is this gravitational subatomic particle flow, once established an creates a format is responsible for spherical to elliptical shaped galaxies. The formation is related to the mass distribution within what is the 3 dimensional spatial galactic core, ultimately it is this area determines the eccentricity of the gravitational subatomic particle field of influence, thus shaping the galactic collection of stellar masses. The black hole, with its compressed mass emitting immense streams along the rotational equator, is responsible for the spiral galaxies. Rotational torque and stream distribution primarily in the black holes provides the spin and definition and number of the spiral arms. As with all universes there will be the odd configurations, where elemental properties of both galactic cores merge in varying degrees.
By passing clusters for simplicity, on the stellar level there is a new layer of field influence established. Most of the deep space gravitational particles due to there extreme charge differential flow back towards the center of the galaxy. Thus, passing through stellar and cosmic objects and applying a force towards the center of flow. Their galactic positions maintained as the repulsion force pushes against the force applied inward by returning gravity particles. A balance occurs within the overall field and equilibrium is established. But lets examine the local stellar zone of influence.
Gravitational subatomic particles with less of a differential from the neutral charge are subject to and can be redirected dependent upon distance from the source and the intensity of the neutral charge flow within the attractant mass. Refresher: the differential is the amount of the neutral charge inherited from the core of the mass as the repulsion particle was ejected from and its subsequent loss of this charge due to time spent in contact with electron stream of dark and elemental matter within the interstellar medium, now as a gravity particle. At the local level gravitational marginally charged particles that would normally flow to the galactic center are slowed and eventually build in zone there is confusion to directional flow towards a new mass with a large enough neutral charge to deflect the natural flow towards the galactic center. This gravitational particle buildup forms the shell or a sub bubble of gravitational field of influence, in which its flow and properties is controlled on the local level by the stellar mass at the center of this bubble. While the bubble itself on a whole is subject to the overall gravitational forces on a galactic level. It is within this bubble that the primary motion of planets and independent cosmic objects are directly affected by the gravitational flow. The repulsive streams and solar wind emitted from a central star or stars that are of a multiple system is contained.
Principles of Gravitational Field Density
The assumption that is a direct attraction between 2 masses that reduces intensity as factor of 4 per a established unit of distance doubles needs to be looked from another perspective. Gravity is a field of subatomic particles flowing towards the dominant mass within the area. As they approach the core of a mass that has not collapsed into a neutron star or black hole the principles follow a simple pattern. Compression increases naturally by a factor of 4 as the spherical volume of the field's radius is halved. So for a mass within the field the distance away from the dominant mass has a direct relationship of the density of gravitational particles flowing through its mass. It is this factor that is responsible for the force, not an attractant wave.
As matter becomes extremely dense, as in neutron stars or black holes, the principles of gravitation field density change exponentially. Normally within the atomic structure of a mass as a gravity subatomic particle passes through the nucleus moves away and the force applied in the direction of movement increases with field density as lateral movement of the various nucleus becomes restricted. Within a neutron star or black hole the gravity particle directly affects the nucleus of matter, which has a cascading affect on the surrounding nuclei as all move as one. Thus the gravitational subatomic particle due to compression of matter increases exponentially. This is the source of the extreme gravitational forces, which is considered weak now able to change the path of a light particle back towards its source.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Equations
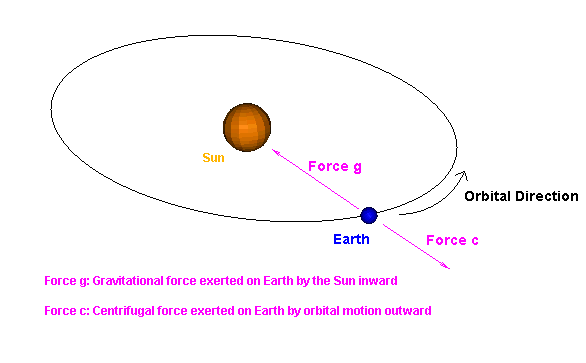
Mankind assumes the force of the Sun's gravity or centripetal force exerted on a planet in orbit is balanced by centrifugal force due to orbital motion. This is not the process. |
Balancing the equations of gravity or centripetal force vs. centrifugal force, we have:
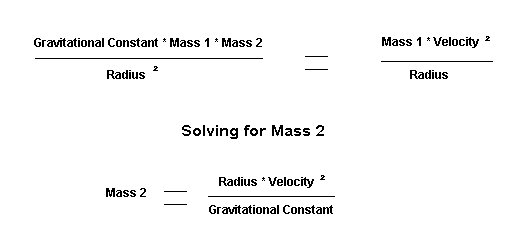
|
The Constants
Mass 1:
The Earth
Mass 2:
The Sun
Gravitational
Constant: 6.67 * 10-11
Radius
(Distance from the Sun to the Earth): 1.4993 * 1011 meters Velocity = Distance * (2 * 3.1416 * Radius) = 29,851 meters / second Time (seconds)
Time
conversion to seconds: 365.25 * 24 * 60 * 60
|
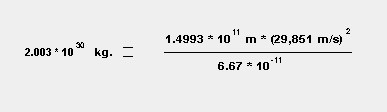 |
Using the same equations on the Earth and the Moon, we can see how the mass for the Earth was approximated at 5.97 * 1024 kilograms. Our answer below is an approximation due to the rounding of distances involving the radius.
|
Mass 1: The Moon Mass 2: The Earth Gravitational Constant: 6.67 * 10-11 Radius (Distance from the Earth to the Moon): 3.85 * 108 meters Velocity = Distance (2* 3.1416 * Radius) = 1024.75 m/sec. Time (seconds) version to seconds: 27 days 7 hours 43 minutes = 2360580
|
Using the same base formula to find the mass of the Sun, we can apply it to find the mass of the Earth.
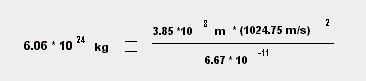 |
|
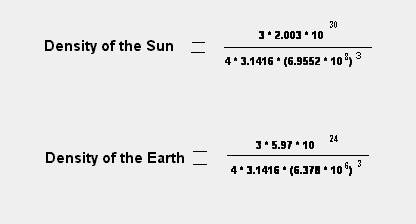
Base Equation
Density
= Mass Volume
|
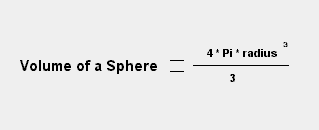 |
|
Reference Radii The Sun: 6.9552 * 108 meters The Earth: 6.378 * 106 meters
|
 |
|
|
Density Reference Density of the mass of the Earth: 5.49
grams/cc. Density of the mass of the Sun: 1.421 grams/cc.
|
The mass of the Earth when compared to the Sun's equated density per cubic centimeter; is too low if compression of matter is to be taken into account. Examining the density of iron, a common element located in the middle of the periodic chart, is a major component within the core of the Earth. Iron has an established density of 7.874 grams/ cc. at 20 degrees C. under normal atmospheric pressure at sea level, but Earthís average density is only 69.76% of iron. With most of the light elements located in the crust, which is about 20 miles thick, and the heavy element residing within the core, how did Newton account for the planetary mass under extreme compression below the crust and within the core of the Earth? One only has to contemplate the depths of the ocean to get an idea of molecular compression, which would crush most reinforced metallic structures on Earth.
Contemplating your questioning established theories of gravity leads to a conclusion that the mass of the Earth is under estimated, which then negates the current approximations of the Sunís mass. If this is so we can show that centrifugal force from planetary orbiting bodies does not balance gravity flowing towards the Sun.
We will conduct a density comparison of equal
volumes of the Sunís and the Earthís masses. Mankind assumes the composition
of the Sun is approximately 71% hydrogen, 27% helium and 1.9% other. This is due to spectrum
analysis of the light emanating from the Sun by astronomers. Most scientists
have overlooked the effects of gravity, light absorption within the stellar mass,
and the surface light overwhelming most internal sources as to be undetected. The
gravitational field intensity within the interior of a solar mass impedes and collects most of the
emitted light
spectrum of the heavy elements emanating from an active core. Only trace amounts of the
heavy elementís spectrum that mixes with the light hydrogen and helium elements
burning in the outer shell are detected giving mankind a false representation
of its true mass composition, which is non homogenous especially within its core.
For those who want a precise break down of the composition of the Sun according to mankindís theories go to http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Tables/suncomp.html
Recreating Mankind's Estimates on Solar Molecular Content
| Element | Density per cm3 @293K in grams | Percentage of element in the Sun | Contribution in mass per cm3 in grams |
| H | 0.00008988 | 71% | .000063815 |
| He | 0.0001787 | 27.1% | .000048428 |
| O | 0.001429 | 0.97% | .000013861 |
| C | 2.62 | 0.40% | .01048 |
| N | 0.00125 | 0.096% | .0000012 |
| Si | 2.33 | 0.099% | .0023067 |
| Mg | 1.738 | 0.076% | .00132088 |
| Ne | 0.0008999 | 0.058% | .000000522 |
| Fe | 7.86 | 0.14% | .011 |
| S | 2.07 | 0.04% | .000828 |
| Totals for 1 gram | --- | Approximately 100% | .026071326 |
Step
1: I will now set up a mathematical proof to shed doubt on the current
estimates of the mass of the Sun and Earth. Setting up an Earth-Sun gravity-mass
comparison, I will use standard measurements established on Earth. Hydrogen and helium at 293
degrees K. under Earthís gravitational force has densities of .00008988 grams
/ cc. and .0001787 grams / cc. respectively at its surface.
Step 2: Establishing the elemental composition and weight of a cubic centimeter of the mass of the Sun on Earth. Reference is available above
Mankind's Reference Material
Columbia University: Hydrostatic Equilibrium
The interior of the Sun is entirely gaseous and the great majority of atoms are stripped of their electrons. The solar gas behaves under these physical conditions nearly like a perfect gas, governed by the "equation of state"
|
|
ďTwo forces keep the Sun in hydrostatic equilibrium in its current stage of evolution: the gravitational force directed inward and the total pressure force directed outward. The equation of hydrostatic equilibrium is "
![]()
where
P is the pressure, r the radial distance from the center, Mr
the mass within a sphere of radius r,
![]() the
matter density, and G the gravitational constant.
the
matter density, and G the gravitational constant.
This equation is consistent with radius changes, but requires the kinetic energy involved in expansion or contraction of the solar body to be small compared to the gravitational potential of the Sun
Source: http://www.columbia.edu/~ah297/unesa/sun/sun-chapter1.html
The equations from Columbia University will be the basis to showing a short fall in gravitational pressure to balance the hydrostatic equation.
Density of elements per cm3 in grams. You can reference data at http://www.vcs.ethz.ch/chemglobe/ptoe/_/1.html
Other
References: http://science.nasa.gov/ssl/pad/solar/interior.htm
The established gravitational acceleration on Earth was 9.8m/sec2 vs. the Sun @
276.16m/sec2 a ratio of
28.1.
Thus the same mass on Earth would exhibit a force
28.1 times greater on the surface of the Sun.
Using Mankindís equation for determining the gravitational acceleration on any mass
|
G * M R2
|
Lets look at the Sun for an example
|
The Constants for our Sun G = 6.67 *
10-11 M = 2.0029
* 1030 R = 6.9552
* 108 |
Following through
and using mankindís
equations what would the gravitational acceleration be if we maintain
the mass containment of the Sun, but reduced its radius at its surface?
|
This table shows how gravitational acceleration would change on the surface of the Sun if we reduced its radius, but its allow the mass to remained static. The current base radius will be represented by 100% and the figures match mankind's current estimates on how many times heavier would a mass on Earth be while on the surface of the Sun. |
Mankind used orbital
velocity to back engineer an estimate for the mass if the Sun when you check against density and
pressures the same equation falls far short or fails due to the Factor
10 Problem. The mass of the Sun is far
greater than mankind assumes and it is ionized nickel-iron core that is
responsible for the Sunís magnetic field which is responsible a majority of the
heavy elements that has pooled at the center of the Sun's mass.
Formula: Force= (Gravitational Constant)*(Mass)/Radius2
Solving for the
gravitational force on Earth, substitute 6.67 * 10-11 for the
gravitational constant, 5.97 * 1024 kg. for the mass of the Earth, and 6.378 *
106 m. for the radius of the Earth.
Plugging in the constants the equation yields a gravitational acceleration force
equal to 9.788837/m2
Using the same equation for the gravitational acceleration on the
surface of Sun
G * M
R2
Substituting the established constants yields
Force= (6.67*10-11) * (2.0029*1030) / (6.9552 *
108 meters)2
Result a gravitational acceleration of 276.16m/sec2
Lets introduce a new equation: Pressure = M/V
for the novice where the variables M = Mass and V = Volume
We will consider how gravitational subatomic particle
field flow and its applied
1.4/.026071326 g cm3 = 53.69 times that on Earth, yet
scientist
know (assume) the gravitational pull on the surface of the Sun is 28.1 times that of
Earth.
If you solve for gravitational force needed it is
525.64/m2
So what reduction in the Sunís radius of the within its mass would be need to be to produced an acceleration of 525.64/m2?
R2 = G * M/F is derived from the original formula F = G
* M/R2
Square Root of (6.67*10-11) * (2.0029*1030)/525.64 yields
5.0377 * 108 new Radius or 72.43% of the Present Sun
So many will counter that the Sun's present radius has expanded due to heat, and this is true. But, with gravity as an established weak force in Earth's text books do you as scientist really expect your definition of gravitational field flow at the surface of our Sun to contain its nuclear reactions and resultant elements transmuted to a plasma state? Are we to return to the dark ages?
Now lets Introduce Another Formula: The Ideal Gas Law
This is the basis for mankind's hydrostatic equation describing the balance of the expansion of stellar interiors and gravitational field force establishing a defined spherical containment, the surface of a star.
|
PV=nRT |
|
The Constants & Variables
P = Pressure V = Volume n =number of moles (Mass) R = Universal Gas Constant (For the brains 8.3145 J/mol K) T = Temperature |
ANALYZING THE EQUATION
|
P=nRT/V |
n is a constant
R is a constant
V is now a constant with a radius 72.43%
We find that temperature in K is directly proportional to pressure, this now complicates matters
So whether I use hydrogen,
helium or any combination, if the volume and mass are constant a rise of 300K
doubles the pressure and so on.
Mankind's best estimate states, that at .25
radii of the Sun, the temperature of the plasma is 7,500,000K with a related density
of 20 g/cm3.
The increase in pressure for
any gas even in a plasma state according to the Ideal Gas law from 300K to 7,500,000 is a
factor of 25,000.
So if we raise the temperature go the original elements that compose the molecular structure of the Sun to just the surface temperature of the Sun 6000K, how does this affect the pressure that gravitational flow counters?
6000 K/293K increases by a factor of 20.47
525.64/m2 (the mankind's definition of
gravitational force needed to compress components
to 1.4) with heat added this rises 20.47 fold
525.64 * 20.47=10759.85
Now using established formulas find the radius at which the total mass of the Sun must be reduced to contain the pressures of an expanding core?
Square Root of (6.67 * 10-11) * (2.0029*1030)/10759.85 yields
1.11426 * 108 new Radius or 16.02% of the Present Sun or well with the core of
the present Sun.
What you have to realize is that current assumptions
related to the mass of the Sun cannot create a
gravitational containment field to contain the fusion process, yet it does exist.
For some, this leads to the
conclusion that the Sun's mass is underestimated.
As inquisitive minds, you are now starting to question current knowledge, it is not about destroying those stuck in the past, but to bring points up as to allow those introduced to a change as if it is was their decision to change, not yours. It is not about us.
A Numerical Simulation of a collapsing nebula cloud does examine the flaws in theoretical star formation giving rise to the Factor 10 deficit associated with compression of stellar matter and its associated gravitational field flow density
You can now conclude the mass of the Sun is underestimated, if so then how can the Earth can maintain its present orbit position with its accepted velocity?
Solving for an unknown constant or
variable
So we have G * Greater M * m/R2 = (m * V2/R) +X
The X factor is an exponential force
based on stream intensity, number of established solar mass streams, distance
between the secondary mass and primary mass. As the masses approach, there is a
back wash of subatomic particle flows that fills the void between the 2 masses.
This builds and eventually applies force pushing the masses apart, which is equal to the missing repulsion force
Thus the basic equation between 2
masses would look like this:
*(Gravitational Constant - Repulsion Constant * e(k * Radius)) Mm/R2= (mV2/R)
But this equation also falls short of explaining of the gravitational interaction between 2 masses as a simple example
a revised equation will shortly follow this revision
This Gravitational Equation is valid only our the Resident Universe
|
Equation Key
|
| With Knowledge Comes Responsibility | I want to thank God, for with out him in my life this paper and its upgrades would have not been possible. | The Meek and Wise Will Inherit |
I want to thank God for bestowing my knowledge
All Rights Reserved: © Copyright 2000, 2004, 2010
Mankind's Explanation for Gravity